Student Projects
Academic Projects in Civil Engineering
Mosaic Tiles with Waste Plastic and Glass Bottles
Mosaic tiles are a type of decorative tile typically composed of small, often colorful pieces of ceramic, stone, or other materials. To reduce plastic and glass wastes and their adverse effect on the environment, they can be utilized in the production of mosaic tiles which has a wearing layer and backing layer. For backing layer, a high-performance mortar is developed by partially replacing cement by 10% silica-fumes and 10% metakaolin and with the addition of 2% steel fibers. The study also investigates the utilization of waste plastic chips in this high- performance mortar with optimum steel fiber and hence various percentages of waste plastic chips (10%, 15%, and 20%) are added and its optimum percentage taken as 20% by analyzing the flexural strength. And the resulting high performance mortar mix with optimum steel fibres and optimum percentage of waste plastic chips is used as backing layer for mosaic tiles whereas wearing layer consists of glass chips embedded in cement marble grout. Average flexural strength of mosaic tiles is obtained as 4.77 N/mm2, whereas average water absorption of mosaic tiles is obtained as 2.46% which satisfies the requirement for flexural strength and water absorption as per IS 1237: 2012. Results of flatness test, perpendicularity test and straightness test also show that they are within the limit as prescribed by IS 1237: 2012.

Eco-Friendly Clay Bricks using Sugarcane Bagasse Ash and Fly Ash
Sugarcane bagasse refers to the fibrous remnants left after extracting juice fromsugarcane or similar plants. Bagasse ash, a byproduct of burning bagasse for energy or otheruses, holds potential in applications like soil enhancement, construction materials, andmanufacturing processes. Similarly, fly ash, a finely powdered byproduct of burning pulverizedcoal in power plants, finds common use in construction due to its ability to strengthenandincrease the durability of materials. Initially, the clay underwent a series of tests includingSpecific Gravity, Natural Water content, Particle Size Distribution, Atterberg’s Limit, Unconfined Compression (UCC), and Proctor Compaction. These tests were conducted to determine the grade and strength of the clay soil. The project then involved adding varying proportions of fly ash by weight of clay, to identify the optimal percentage through tests like Unconfined Compression (UCC) and proctor compaction again. Subsequently, different proportions of sugarcane bagasse by weight of clay were introduced to the mixture established through the prior tests. The most suitable values for both additives are determined based on the outcomes of these tests, guiding the preparation of the final brick composition. Finally, a brick was developed as the end result of this project which is equivalent to class C of burnt brick and it can be used for temporary structures like non load bearing walls, partition walls, infill walls, decorative purposes etc.

Development of Bioplastic from Organic Solid Waste
Organic solid waste is an environmental threat worldwide. However, the organic waste has a great potential for the generation of fuels and high value products. Bioplastics are 100% bio-degradable, compostable or recyclable free from hazardous chemical and toxic substance. Bioplastics can significantly reduce the environmental impact in terms of energy consumption and greenhouse effect. Utilizing organic solid waste as a feedstock of plastics production, offers multiple advantages. It helps to reduce waste and prevent landfill or incineration and related pollution. It also provides a circular economy approach by transforming waste into valuable materials. One such solution is to convert organic fraction of organic solid waste into bioplastic, which will be environment friendly. The project is focused on the conversion of organic fraction of solid waste into bioplastic.

Smart Sprinkler Irrigation System
Water scarcity in agriculture can lead to soil salinization, alkalization, and environmentaldegradation; therefore, this study aims to propose an IoT-based smart irrigation system toreduce water consumption and control efficiency in agriculture. A sensor-enabled smartsprinkler irrigation system was created. The optimum moisture content of the soil was foundfor the calibration of sensors and for determining other irrigation parameters like field capacity, permanent wilting point, irrigation interval, etc. A water test was done todetermine the pH of the water to ensure that it was suitable for agricultural purposes. Thetruth table for deciding whether irrigation was needed or not was developed by collectinghourly weather data for several days. The performance of the smart sprinkler was evaluatedby findingsprinkler uniformity and efficiency using case studies.A web application was developed withthe help of embedded C to remotely turn on and offsprinklers, set watering times, and adjustthe watering schedule based on soil moisturelevels. This web application controls irrigationand supplies the appropriate amount ofwater from the pump. A microcontroller monitoredtemperature, humidity, and soilmoisture to calculate plant water requirements, which is usableand effective on Androidsmartphones. This project optimises water usage, improves cropyields, and conservesresources, reducing water wastage and the inefficient use of resourcesin traditionalmethods.

Brick with Plastic Waste and C&D Waste
Bricks have been a significant construction and building material for a long time and are widely used around the world. Traditional masonry bricks are made of clay burnt under high temperatures, resulting in high energy consumption, environmental contaminations and decreased natural raw materials. So in order to limit nature risks, inorganic materials such as plastic waste and construction demolished waste can be used to produce bricks. It is estimated that the construction industry generates about 10-12 million tons of construction waste and nearly 300 million tons of plastic wastes annually, which cause a threat to the environment. So the introduction of new technologies to recycle and convert waste into useful materials is crucial for environmental protection and sustainable development. The study deals with an experimental investigation on the use of plastic waste and construction demolished waste in brick manufacturing. The re- utilization of waste materials in brick production can be a successful strategy in terms of less water absorption, waste production reduction as well as decreased clay utilization. This project aims at establishing the optimum percentage of plastic waste in construction demolished waste by adding various percentages of plastic (20%, 25%, 30%) in construction demolished waste based on compressive strength and water absorption property.

A Mobile Application to Analyse Performance of Excavation Equipment
Performance is a numerical measurement of quality of an equipment or process assessed through measurement of physical products and statistical sampling of the output of processes. Excavation equipment are heavy-duty vehicles specifically created for carrying out construction activities, most usually including earthwork operations. Excavators, Backhoe loaders are the most common equipment’s used for excavation in the construction industry. Defects or lapses in the performance of such equipment can lead to increased costs and delays in project completion. This project involves the identification of the factors that affect the performance of excavation equipment in multistorey residential building construction sites. After the identification of these factors, analysis is done and the major factors that affects the performance are ranked. After identifying and ranking the factors, a model is prepared and a mobile application consist of login page, excavation data page, excavation calculator page is developed to examine the performance of excavation equipment.

Equipment for Reducing Ergonomic Risk in Construction Workers
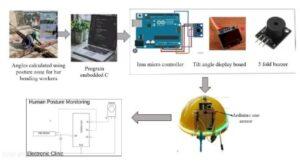
Construction industry is one of the highly risky industries with more number of accident and injuries. The increasing number of injuries caused by repetitive motion, excessive force and awkward postures, ergonomics has become a critical factor in workplace safety. All the employees have a risk of injury when working due to the unawareness with the applicable regulations. Based on the literature, the most significant ergonomic risk aspects are awkward posture in handling job task, force and repetition of specific movement including vibration and noise. Other ergonomics riskaspects includes uncomfortable static position, contact stress of muscles and tendon and also extreme temperature and environment conditions, this increases stress level which is significantly related with musculoskeletal disorders. Among these repetition which involves in doing a task that uses the same muscles over and over with little chance for recovery or working in extreme temperature condition either extremely cold and extremely hot also are the main risk factors. The posturesrelated to the corresponding works is find out by taking their live images during their work using the Software POSTUREZONE. For more accuracy the same worker’s posture from different sides are find out and after that angles obtained is collected for assessing risk using REBA worksheet. REBA is a sensitive tool for assessing abnormalities in all parts of the body (wrists, upper arms, forearms, neck, trunk, and legs). In this project risk is analyzed using work sampling observation area made on workers involved in the task. The hazards are then evaluated using plastering, flooring, reinforcing bar. REBA Score is then developed to describe the posture, repetition of work and the level of risk. In this method ergonomic risk factors are identified based on checklist or score. Based on the assessment an alert system is developed for repetitive task therefore the main causes of injury experienced are identified. It can provide comprehensive results in determining a good work position and it can minimize the risk of work accidents for operators when working.
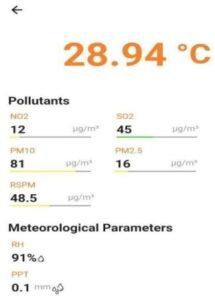
Mobile Application for Analysing Air Temperature
Temperature variation in the atmosphere is closely related to climatic change, environmental pollution and human health. It has become the prime concern of most countries due to the anthropogenic activities and adverse meteorological situations. This temperature variation depends on various factors like the meteorological parameters as well as the air pollutants. The analysis of temperature variation with these factors are done using Geographically Weighted Regression Modelling (GWR) in Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS). This idea is used to study the chronographic change of relationship between a dependent attribute and one or more independent attribute from the output obtained from GWR modelling in SPSS Software. In this study the variation of air temperature is analyzed with pollutants and meteorological parameters. The study area chosen are Vytila, MG Road, Eloor, Methanam, Kalamasserry. The concentration of NO2, SO2, Respirable suspended particulate matter (RSPM) and the meteorological parameters like Relative humidity, precipitation and atmospheric temperature over 2010-2020 were collected from Kerala pollution control board and meteorological department respectively. A numerical model was developed using the above data to study the variation of temperature in the selected areas. Using this numerical model, a mobile application “TEMPCALC” was developed for analyzing air temperature variation.
Groundwater Quality Mapping of Mulanthuruthy Grama Panchayat using GIS
Team Members: Afrin Siyad, Sreelakshmy R Nair, Gabri Siby, Sandhra Ajayakumar
Guided by: Asst. Prof. Mary Dhanya
About Project: Groundwater is an important component of our nation’s fresh water resources.In this project, groundwater quality of Mulanthuruthy Gramapanchayath, Ernakulam Dist. (Kerala)is assessed and mapping is carried out to analyse the quality of groundwater. For the study, a total of 64 well water samples (4 samples each from 16 wards) are collected from Mulanthuruthy Gramapanchayath. The samples are analysed by testing the various physicochemical characteristics including pH, chloride, sulphide, total hardness, turbidity, fluoride, nitrate, E. coli and ammonia of water samples. The ArcGIS 10.5 is preferred for the generation of various thematic maps and final groundwater quality mapping is prepared based on Water Quality Index (WQI). The purpose of this project is to provide an overview of present groundwater quality, to determine spatial distribution of groundwater quality parameters and to map groundwater quality based on WQI using GIS.

Achievements
Project is funded by the Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment (KSCSTE)
Experimental Investigation of Porous Concrete Using E-Waste
Team Members: Alen Reji, Archa Dileep, Aiswarya Manikandan, John Varghese
Guided By: Asst. Prof. Sangeetha S
About project: Discarded, obsolete, and unusable electronic equipment is known as electronic waste or E-waste. Efforts are made in the construction industry to use the non-biodegradable components of E-waste as a partial replacement for coarse aggregates or fine aggregates in concrete. The major objective of this project is to reduce the accumulation of used and discarded electronic equipment as much as possible. The study was conducted on porous concrete, which is a special variety of concrete with high porosity created from a mixture of cement, coarse aggregates, and water. Mix proportion of porous concrete block was 1: 0: 2.54. E-plastic waste was used to replace 0%, 10%, 15%, and 20% of the coarse aggregates in porous concrete. The developed product can be used as a pavement block so that the accumulation of rain water can be reduced.

Porous Concrete Block using E – Waste
Achievements
Project funded by The Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment(KSCSTE)
Experimental Investigation on Self-Healing Bituminous Concrete
Team members: Ashmy Babu V, Eldho Biju, Favaz Roshan K Z, Amal Thomas
Guided by: Asst. Prof. Jesna NM
About project: High traffic conditions and lack of proper maintenance leads to formation of cracks in the roads. As the time progresses these cracks increases and lead to pothole formation and finally disintegration ofroads and surface wear takes place. This makes difficult for the passengers to travel and increases accident rates on roads. In order to solve this problem,a self-healing bituminous concrete is made by adding waste steel fibres to bituminous concrete. Addition of waste steel fibres to bituminous concrete ensures that it becomes conductive and the cracked surface get healed with induction heating rather than reconstructing the pavement. In this study, a bituminous concrete mix with waste steel fibres having the ability to heal cracks under the application of heat was prepared and Marshall properties of the same wereanalysed with an induction heating apparatus developed as part of the project.

Induction Heating Apparatus
Achievements
- Developed anInduction Heating Apparatus to check the Marshall properties of the mix.
- Published a paper:Amal Thomas, Ashmy Babu V, Eldho Biju, Favaz Roshan K Z, Jesna N M (2022); A Review on Self Healing Technologies used in Bituminous Concrete, International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews, Volume 9, Issue 2, pp 924-927.
Development of Waste Water Filter using Groundnut Shell and Rice Husk to Treat Heavy Metals
Team members:D Viswalakshmi, Sarah Ali P A, Ashique K Kunjumon, Serene C J
Guided by: Asst.Prof. Archana CP
About project: Industrial wastewater produced during manufacturing process or cleaning activities is toxic as it contains heavy metals in dissolved form. Experiments have been conducted to develop simple and environment friendly wastewater treatment methods. In this study, activated rice husk and groundnut shell are used to modify the sand filter to remove the heavy metals from the wastewater. Groundnut shell and rice husk are agro based waste materials which are environment friendly and easily available. Modification of the sand filter was done by partial replacement of sand and gravel. Synthetic wastewater was prepared using heavy metals like cadmium, chromium, copper, iron, lead separately and then passed throughsand filter and modified sand filter to compare the efficiency to remove heavy metals from wastewater. It was found that the efficiency of the modified sand filter with agro based waste materials like groundnut shell and rice husk was much higher than the conventional sand filter.

Achievements
- Published a paper: Ashique K Kunjumon, D Viswalakshmi, Sarah Ali P A, Serene C J, Archana C P (2022); Removal of heavy metals using natural adsorbents- A review, International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR)
- Design of Cable Stayed Bridge
Team members: Megha Sajeev, Nihal Babu, Sayanth, Sreelakshmi S Shajan
Guided by: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Smitha K K
About Project: A bridge is a structure which is built over some physical obstacle such as a body of water, valley, or road, and its purpose is to provide crossing over that obstacle. It is built to be strong enough to safely support its own weight as well as the weight of anything that should pass over it. A cable stayed bridge is a structure in which the span of bridge is supported by inclined cables connected to the towers. The load from the bridge is transferred to the towers through cables and from there it is transferred to foundation. The project proposes the design of a Cable stayed Bridge across Bharathapuzha at Ponnani where the river merges with Arabian Sea usinga structural analysis and design software SAP2000.

3 D Model of the Proposed Bridge
Achievements
- Megha Sajeev, Nihal Babu, Sayanth, Sreelakshmi S Shajan,Smitha K K, Analysis of Cable Stayed Bridge Proceedings of SRISHTI 2022, Saingits College of Engineering Pathamuttam, Kottayam, Kerala, ISBN 978-93-5680-852-2, pp CE 120-CE 123.
M.Tech Projects 2021-2022
Civil Construction Subcontractor Selection using Fuzzy Logic in MATLAB
Submitted by: Femin Maria I X
Guided by: Asst. Prof. Basil S Jacob
About project: Subcontractors play an important part in the success of construction projects. Selection of an appropriate subcontractor considering multiple criteria is a crucial challenge faced in construction industry. In reality, the application of the classic multi-criteria decision-making methods has various practical constraints in the selection process. The overall aim is to implement a fuzzy logic-based decision model for the selection of civil construction subcontractor using MATLAB software. The study takes an integrated approach that links the relative importance index method into fuzzy logic technique. The model implementation provides a way to improve the process for assessing and selecting subcontractors, which avoids the failure of projects due to inefficient subcontractor thus attaining project success.
Achievements
- Published paper: Femin Maria I X and Basil S Jacob (2022); Analysis on the criteria influencing subcontractor selection of multistoried residential buildings in Kerala using relative importance index method, International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews, 9(2), 308-312.
Application of Lean Principles in Multi-Storeyed Building Construction
Submitted by: Yedulakshmi Nair
Guided by: Asst. Prof. Archana C.P
About Project: The construction process involves value-added activities and non-value-added activities (NVA). NVA are those which do not add any value during the construction process. Lean construction is one of the project management techniques that has been used to increase performance in the construction sector. The most significant Lean application objective is to find non-value-added activities on construction projects, which is possible using a number of Lean tools. This project aims to identify the critical factors that lead to non-value-added activities based on seven wastes, as well as to assess labour inefficiency and cost of labour inefficiency caused by the seven lean wastes that have been identified and measured through direct observations in column, staircase, beam &slab concreting using the work sampling method. The project develops a work sampling tool mobile application to easily generate the monitoring time, pausing time, setup time and the amount of time spent by labour on different wasteful activities in a direct graphical format.
Achievements
- Published a paper:Yedulakshmi Nair, Archana C.P (2022), Analysis of Factors Leading to Non-Value-Added Activities in Multi-Storeyed Building Construction Using Lean Technology, International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews, Vol 9, Issue 2,848-856.
Prediction Model for Schedule, Cost Variance in Road Construction Projects Using ANN
Submitted by: Taneya Tom
Guided by: Chithra C J
About project: Modelling of cost and schedule variance of a road will be helpful for members of the construction project to understand the factors, which they must closely monitor to complete the project with the required performance. Questionnaire survey is done to find the most influencing factors affecting cost and schedule variance of road projects and RII is used to rank the factors. The most influencing factors on cost variance were identified such as fluctuation of material price, poor planning, scheduling and monitoring, increasing labour salaries, fluctuation of plant and machineries cost, project site location, mistakes in the estimation of cost for the project, design changes during construction, poor site management at siteand slow decision process. Most influencing factors on schedule variance were identified as weather conditions, shortage in construction materials, slowness of the owner decision making process, poor site management and supervision by contractor, construction methods, ineffective planning & scheduling of project by contractor, geological problems on site. Analysis is done to find out the factors which are highly correlated with the cost and schedule variance. An Artificial Neural Network model is developed to predict the schedule and cost variance in road construction projects. The trained network’s performance is evaluated using Mean Square Error and Regression Analysis.
Achievements
- Published a paper: Taneya Tom, Chithra C J (2022), Prediction Model for Schedule, Cost Variance in Road Construction Projects using ANN, International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews, Volume 9, Issue 3, 683-696.
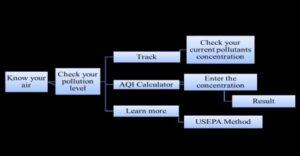
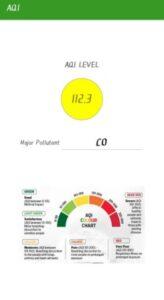
Air Quality Index (AQI) Calculator
Air Quality Index (AQI) is a simple and commonly used method to evaluate the overallair pollution of a region. The overall AQI can give clear view about ambient air and thecritical pollutant mainly responsible for the quality of air, which can be easier for acommon man to understand.Air Quality in various parts of Ernakulam city is being regularly monitored by Kerala State Pollution Control Board. The pollutant’s concentration data were collected and AQIswere calculated to assess the ambient air quality at three selected areas namely Eloor(Industrial), Vyttila (Commercial) and M.G. Road (Residential) areas of Ernakulam cityduring the year 2018, 2019 &2020. The AQIs were calculated according to Indian Airquality Index (IND-AQI).The AQI study reveals that particulate matter (PM2.5 &PM10) was mainly responsible for maximum times in all selected areas of Ernakulam city. The AQIs obtained were used to analyse the quality of air before, during and after the lockdown 2020.A web-based AQI app using android software was developed and AQI of the selectedareas were analysed. The efficiency of the AQI calculator app was validated bycomparing the manually calculated AQI and AQI calculated using the application. Theapplication was developed for quick, simple and an elegant looking response to an AQIonline query.