Product Development
2024- 2025
Improving Construction Site Safety Using Smart Insole
Working personnel on construction sites experience the highest occupational risks throughouttheir shifts, especially when fall incidents, machine-related accidents and hazardousenvironmental conditions are combined. These risks create significant occupational safetythreats and directly impact project schedules and operational productivity. This Projectpresents a unique fusion of wearable technology with automated foot-structure devices thatperform obstacle detection and movement tracking simultaneously. The smart insole consistsof tracking sensors that monitor worker activities while also detecting objects in operationalareas. The system enables immediate data collection to assess current site safety conditions,allowing preventive actions to be taken before accidents occur. This proactive monitoringapproach enhances worker safety at the workplace through its ability to create a safer buildingenvironment with reduced project risks. The developed software solutions enable the smartinsole to generate instant visual representations of worker movements together with hazardpositions found in the workplace. The software provides real-time site condition updates,allowing safety personnel and construction managers to detect hazards and implement rapidsafety measures. The system facilitates safety assessments by analyzing safety patterns,leading to informed decisions about safety protocols. This connected technology systemenables realtime worker surveillance, promptly detecting incidents and creating protectivework environments within the construction sector.
Greywater Treatment Using Neem Leaf, Banana Peel and Guava Leaf
Water is the most ubiquitous material in nature and most vital for domestic purposes suchasdrinking, cooking, washing, bathing etc. Water treatment (WT) is currently among the majorareas of research due to the depletion of water resources and fear mongering regardingenvironmental pollution, which has compelled the upgrading of conventional WTtechnologytowards recycling and reuse. In this project we use the powder of Neem leaf, Dried Banana peel and Guava leaf as coagulants to treat the greywater from the kitchen. This work providesinformation related to natural bio-coagulants such as Neem leaf, Dried Banana peel andGuavaleaf powder and their merits and limitations, outlines the performance of turbidity of greywaterby adding different proportions of coagulants and highlights their efficiency of coagulationmechanism, turbidity removal, pH and colour. Although chemical coagulants are efficient inWT, they are usually expensive, toxic, associated with health issues and non-sustainable. So,thesustainable alternative is the use of natural coagulants such as Neem leaf, Dried Banana peel andGuava leaf powder which are readily available, economical, easy to use, biodegradable, nontoxic, eco-friendly and effective. It could be concluded that the natural bio coagulants havetheability to remove turbidity greatly in waste water, hence it has a great potential toreplacechemical coagulants in greywater water treatment.
Sustainable Domestic Sewage Treatment Unit Using Canna Indica
Domestic sewage water, which originates from household sources such as kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry, poses a significant environmental risk due to its harmful contaminants, including organic pollutants and oil and grease, particularly in kitchen wastewater. This project aimed to develop a sustainable domestic sewage treatment unit using Canna indica for treating kitchen wastewater from the college canteen. The treatment system included key components such as an oil and grease trap, anaerobic digester, aeration tank, and a constructed wetland planted with Canna indica. Initial parametric analysis showed that the levels of BOD, COD, nitrogen, phosphorus, oil and grease, and TSS were above the permissible limits set by the CPCB, necessitating an effective treatment solution. After anaerobic digestion, BOD and COD levels reduced by 87.4% and 88.2%, respectively, while oil and grease were completely removed. After 24 hours of retention in the Canna indica wetland, BOD and COD were reduced by 90% and 91.65%, respectively, and nitrogen removal reached 74.19%. After a 5-days of retention period, the system achieved a 95% reduction in BOD, 93.89% reduction in COD, 96.59% reduction in nitrogen, and complete removal of TSS, phosphorus, and oil and grease. The synergistic action of Canna indica and the microbial consortium of Pseudomonas putida and Rhodobacter enhanced pollutant removal through phytoremediation, microbial degradation, and filtration. The results validate the system’s potential as an efficient, eco-friendly solution for domestic wastewater treatment, demonstrating consistent pollutant removal.
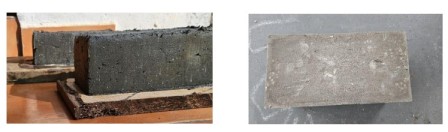
Eco-Friendly Marine Clay Bricks Using Chitosan Biopolymer and Alccofine
The construction industry is increasingly seeking sustainable materials to reduce its environmental impact. Sand, cement, coarse aggregate for manufacturing of bricks and used for large construction activities are energy intensive as well as causing environmental pollution during their entire life cycle. This project explores the development of eco-friendly marine clay bricks incorporating chitosan biopolymer and Alccofine. Marine clay is a type of fine-grained soil typically found in coastal, estuarine, and marine environments. Chitosan, derived from chitin in shrimp and crab shells, is selected for its biodegradability and binding properties, while Alccofine is an eco-friendly and low calcium silicate- based material highly processed and obtained from GGBS, the waste material generated from iron ore. Initially, a series of tests including water content, consistency limits, particle size distribution and Unconfined Compression test (UCC) will be conducted to assess the properties of the marine clay. The project then involves adding 1% conc. chitosan biopolymer solution to various proportion of Alccofine 5%,10%,15%,20% by the weight of clay to identify the optimum percentage of Alccofine through UCC test. Based on the mix proportion obtained from the previous tests brick of size 19 x 9 x 9 cm will be cast and air cured for 28 days. Finally, tests such as compressive strength, water absorption, hardness, soundness of the brick shall be conducted to check the suitability of this brick in building construction.
Carbon Negative Concrete Paver Block UsingFerrock
As the construction industry is a leading contributor to carbon emissions, innovative solutions to achieve sustainability has to be developed. The scope of this project is to highlight the potential of using ferrock, an iron-based binder material, known for its ability to absorb and sequester carbon dioxide during curing, as a sustainable substitute for ordinary Portland cement. By the replacement of cement with optimum percentage of ferrock in concrete, the proposed paver blocks can significantly reduce the carbon footprint by absorbing CO2 while enhancing mechanical properties and durability. Various literatures suggests that the optimum percentage of ferrock in concrete was 8-10% by weight of cement based on various strength and durability tests. Also, durability problems such as alkali-aggregate reactivity, sulphate & chloride attacks, reinforcement corrosion etc. can be controlled by improving the properties of conventional concrete by the incorporation of ferrock. This project aims at developing carbon negative concrete paver blocks by using M30 concrete mix incorporating optimum percentage of ferrock. The purpose of the project is to look into the durability and mechanical properties of prepared paver blocks. The optimum percentage of ferrock in the mix was 9%, and several tests were performed on paver blocks to determine compressive strength, tensile splitting strength, flexural strength, water absorption and abrasion resistance. All the tests’ results demonstrated significant improvement in strength when compared to conventional concrete paver block. The water absorption was also found to decrease while replacing cement with ferrock. These findings emphasize the potential of ferrock to be used as a sustainable replacement for cement in paver block.
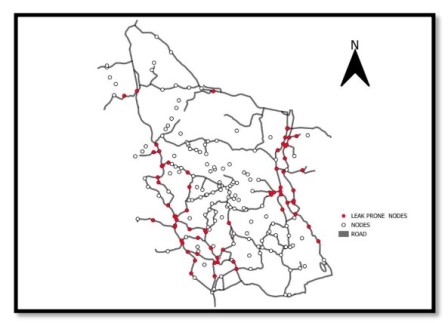
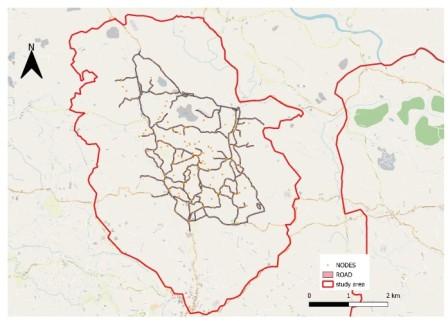
PREDICTIVE MODEL FOR IDENTIFYING POTENTIAL LEAKS IN THE UNDERGROUND WATER PIPELINE NETWORK
The efficient management of underground water pipeline networks is essential for ensuring a reliable water supply in urban areas. This study focuses on developing a predictive model for identifying potential leaks in an underground water pipeline network. The approach integrates Geographic Information System (GIS) technology with EPANET software to analyze and visualize the spatial characteristics of the water distribution network. Initially, the study examines the existing water supply system within the designated study area, gathering relevant data on pipeline locations, diameters, and historical leak occurrences. Using this data, a distribution network is designed and modeled in EPANET, which simulates hydraulic behavior under various operational conditions. To enhance the predictive capability, the GIS map created from the EPANET model is employed for spatial analysis, enabling the visualization of areas with a higher likelihood of leaks. The model is then trained using real-world data, including pressure fluctuations, pipe material properties, and historical leak records, to identify patterns indicative of potential leaks. The effectiveness of this predictive model is evaluated by applying it to the study area and comparing the predicted leaks with actual leak occurrences. The results demonstrate that the model can significantly improve the detection of potential leaks, thereby facilitating timely maintenance and reducing water losses.
BENDABLE CONCRETE SLAB
Bendable concrete also known as Engineered Cementitious Composite (ECC) is an innovative building material designed to exhibit high ductility and flexibility, allowing it to bend and deform under stress without cracking. The study aims to evaluate the load-bearing capacity, deflection characteristics, crack propagation patterns, durability and overall performance of RC slab made of bendable concrete with various types and proportions of fibres (including polyvinyl alcohol, coconut fiber and carbon fibres) under static load. The findings will be compared to traditional concrete to highlight the advantages of using bendable in construction, with a focus on enhancing durability, and structural performance. The results of this study will contribute to the development of more resilient and sustainable building materials, with potential applications in a wide range of infrastructure and construction projects.
2023- 2024
Mosaic Tiles with Waste Plastic and Glass Bottles
Mosaic tiles are a type of decorative tile typically composed of small, often colorful pieces of ceramic, stone, or other materials. To reduce plastic and glass wastes and their adverse effect on the environment, they can be utilized in the production of mosaic tiles which has a wearing layer and backing layer. For backing layer, a high-performance mortar is developed by partially replacing cement by 10% silica-fumes and 10% metakaolin and with the addition of 2% steel fibers. The study also investigates the utilization of waste plastic chips in this high- performance mortar with optimum steel fiber and hence various percentages of waste plastic chips (10%, 15%, and 20%) are added and its optimum percentage taken as 20% by analyzing the flexural strength. And the resulting high performance mortar mix with optimum steel fibres and optimum percentage of waste plastic chips is used as backing layer for mosaic tiles whereas wearing layer consists of glass chips embedded in cement marble grout. Average flexural strength of mosaic tiles is obtained as 4.77 N/mm2, whereas average water absorption of mosaic tiles is obtained as 2.46% which satisfies the requirement for flexural strength and water absorption as per IS 1237: 2012. Results of flatness test, perpendicularity test and straightness test also show that they are within the limit as prescribed by IS 1237: 2012.

Eco-Friendly Clay Bricks using Sugarcane Bagasse Ash and Fly Ash
Sugarcane bagasse refers to the fibrous remnants left after extracting juice fromsugarcane or similar plants. Bagasse ash, a byproduct of burning bagasse for energy or otheruses, holds potential in applications like soil enhancement, construction materials, andmanufacturing processes. Similarly, fly ash, a finely powdered byproduct of burning pulverizedcoal in power plants, finds common use in construction due to its ability to strengthenandincrease the durability of materials. Initially, the clay underwent a series of tests includingSpecific Gravity, Natural Water content, Particle Size Distribution, Atterberg’s Limit, Unconfined Compression (UCC), and Proctor Compaction. These tests were conducted to determine the grade and strength of the clay soil. The project then involved adding varying proportions of fly ash by weight of clay, to identify the optimal percentage through tests like Unconfined Compression (UCC) and proctor compaction again. Subsequently, different proportions of sugarcane bagasse by weight of clay were introduced to the mixture established through the prior tests. The most suitable values for both additives are determined based on the outcomes of these tests, guiding the preparation of the final brick composition. Finally, a brick was developed as the end result of this project which is equivalent to class C of burnt brick and it can be used for temporary structures like non load bearing walls, partition walls, infill walls, decorative purposes etc.

Development of Bioplastic from Organic Solid Waste
Organic solid waste is an environmental threat worldwide. However, the organic waste has a great potential for the generation of fuels and high value products. Bioplastics are 100% bio-degradable, compostable or recyclable free from hazardous chemical and toxic substance. Bioplastics can significantly reduce the environmental impact in terms of energy consumption and greenhouse effect. Utilizing organic solid waste as a feedstock of plastics production, offers multiple advantages. It helps to reduce waste and prevent landfill or incineration and related pollution. It also provides a circular economy approach by transforming waste into valuable materials. One such solution is to convert organic fraction of organic solid waste into bioplastic, which will be environment friendly. The project is focused on the conversion of organic fraction of solid waste into bioplastic.

Smart Sprinkler Irrigation System
Water scarcity in agriculture can lead to soil salinization, alkalization, and environmentaldegradation; therefore, this study aims to propose an IoT-based smart irrigation system toreduce water consumption and control efficiency in agriculture. A sensor-enabled smartsprinkler irrigation system was created. The optimum moisture content of the soil was foundfor the calibration of sensors and for determining other irrigation parameters like field capacity, permanent wilting point, irrigation interval, etc. A water test was done todetermine the pH of the water to ensure that it was suitable for agricultural purposes. Thetruth table for deciding whether irrigation was needed or not was developed by collectinghourly weather data for several days. The performance of the smart sprinkler was evaluatedby findingsprinkler uniformity and efficiency using case studies.A web application was developed withthe help of embedded C to remotely turn on and offsprinklers, set watering times, and adjustthe watering schedule based on soil moisturelevels. This web application controls irrigationand supplies the appropriate amount ofwater from the pump. A microcontroller monitoredtemperature, humidity, and soilmoisture to calculate plant water requirements, which is usableand effective on Androidsmartphones. This project optimises water usage, improves cropyields, and conservesresources, reducing water wastage and the inefficient use of resourcesin traditionalmethods.
2022- 2023
Brick with Plastic Waste and C&D Waste
Bricks have been a significant construction and building material for a long time and are widely used around the world. Traditional masonry bricks are made of clay burnt under high temperatures, resulting in high energy consumption, environmental contaminations and decreased natural raw materials. So in order to limit nature risks, inorganic materials such as plastic waste and construction demolished waste can be used to produce bricks. It is estimated that the construction industry generates about 10-12 million tons of construction waste and nearly 300 million tons of plastic wastes annually, which cause a threat to the environment. So the introduction of new technologies to recycle and convert waste into useful materials is crucial for environmental protection and sustainable development. The study deals with an experimental investigation on the use of plastic waste and construction demolished waste in brick manufacturing. The re- utilization of waste materials in brick production can be a successful strategy in terms of less water absorption, waste production reduction as well as decreased clay utilization. This project aims at establishing the optimum percentage of plastic waste in construction demolished waste by adding various percentages of plastic (20%, 25%, 30%) in construction demolished waste based on compressive strength and water absorption property.
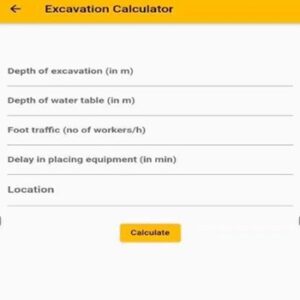
A Mobile Application to Analyse Performance of Excavation Equipment
Performance is a numerical measurement of quality of an equipment or process assessed through measurement of physical products and statistical sampling of the output of processes. Excavation equipment are heavy-duty vehicles specifically created for carrying out construction activities, most usually including earthwork operations. Excavators, Backhoe loaders are the most common equipment’s used for excavation in the construction industry. Defects or lapses in the performance of such equipment can lead to increased costs and delays in project completion. This project involves the identification of the factors that affect the performance of excavation equipment in multistorey residential building construction sites. After the identification of these factors, analysis is done and the major factors that affects the performance are ranked. After identifying and ranking the factors, a model is prepared and a mobile application consist of login page, excavation data page, excavation calculator page is developed to examine the performance of excavation equipment.
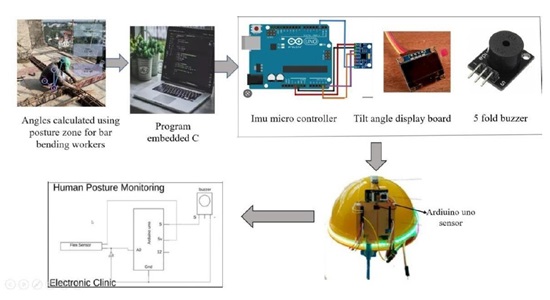
Equipment for Reducing Ergonomic Risk in Construction Workers
Construction industry is one of the highly risky industries with more number of accident and injuries. The increasing number of injuries caused by repetitive motion, excessive force and awkward postures, ergonomics has become a critical factor in workplace safety. All the employees have a risk of injury when working due to the unawareness with the applicable regulations. Based on the literature, the most significant ergonomic risk aspects are awkward posture in handling job task, force and repetition of specific movement including vibration and noise. Other ergonomics risk aspects includes uncomfortable static position, contact stress of muscles and tendon and also extreme temperature and environment conditions, this increases stress level which is significantly related with musculoskeletal disorders. Among these repetition which involves in doing a task that uses the same muscles over and over with little chance for recovery or working in extreme temperature condition either extremely cold and extremely hot also are the main risk factors. The posturesrelated to the corresponding works is find out by taking their live images during their work using the Software POSTUREZONE. For more accuracy the same worker’s posture from different sides are find out and after that angles obtained is collected for assessing risk using REBA worksheet. REBA is a sensitive tool for assessing abnormalities in all parts of the body (wrists, upper arms, forearms, neck, trunk, and legs). In this project risk is analyzed using work sampling observation area made on workers involved in the task. The hazards are then evaluated using plastering, flooring, reinforcing bar. REBA Score is then developed to describe the posture, repetition of work and the level of risk. In this method ergonomic risk factors are identified based on checklist or score. Based on the assessment an alert system is developed for repetitive task therefore the main causes of injury experienced are identified. It can provide comprehensive results in determining a good work position and it can minimize the risk of work accidents for operators when working.
Mobile Application for Analysing Air Temperature
Temperature variation in the atmosphere is closely related to climatic change, environmental pollution and human health. It has become the prime concern of most countries due to the anthropogenic activities and adverse meteorological situations. This temperature variation depends on various factors like the meteorological parameters as well as the air pollutants. The analysis of temperature variation with these factors are done using Geographically Weighted Regression Modelling (GWR) in Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS). This idea is used to study the chronographic change of relationship between a dependent attribute and one or more independent attribute from the output obtained from GWR modelling in SPSS Software. In this study the variation of air temperature is analyzed with pollutants and meteorological parameters. The study area chosen are Vytila, MG Road, Eloor, Methanam, Kalamasserry. The concentration of NO2, SO2, Respirable suspended particulate matter (RSPM) and the meteorological parameters like Relative humidity, precipitation and atmospheric temperature over 2010-2020 were collected from Kerala pollution control board and meteorological department respectively. A numerical model was developed using the above data to study the variation of temperature in the selected Jareas. Using this numerical model, a mobile application “TEMPCALC” was developed for analyzing air temperature variation.
2021- 2022
Porous Concrete Block using E-waste
Modern scientific and technological advancements have altered the way of living of the common man. Instead of going through the trouble of having an old appliance repaired, most would prefer to get a new one. Such a trend not only leads to an increase in the volume of electronic waste but also poses a serious threat to public health and the environment. Discarded, obsolete, and unusable electronic equipment is known as electronic waste or E-waste. Efforts are made in the construction industry to use the non-biodegradable components of E-waste as a partial replacement for coarse aggregates or fine aggregates in concrete. The major objective of this project is to reduce the accumulation of used and discarded electronic equipment as far as possible. The study was conducted on porous concrete, which is a special variety of concrete with high porosity created from a mixture of cement, coarse aggregates, and water. Mix proportion of porous concrete block was 1:0:2.54. E-plastic waste was used to replace 0%, 10%, 15%, and 20% of the coarse aggregates in porous concrete.
Achievements
Project funded by The Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment (KSCSTE)
Waste Water Filter using Groundnut Shell and Rice Husk to treat Heavy Metals
Wastewater is produced from various sources like households, farms, and industries. Industrial wastewater is produced during the manufacturing process or the cleaning activities related to the process. It is toxic as it contains heavy metals in dissolved form. Wastewater treatment and disposal is a serious issue to look into. Recently, experiments have been conducted to develop simple and environment friendly wastewater treatment methods. In this study, activated rice husk and groundnut shell are used to modify the sand filter to remove the heavy metals from the wastewater. Groundnut shell and rice husk are agro based waste materials which are environment friendly and easily available. Modification of the sand filter was done by partial replacement of sand and gravel. The synthetic wastewater was prepared using heavy metals like cadmium, chromium, copper, iron, lead separately and then passed through both sand filter and modified sand filter to compare the efficiency to remove heavy metals from wastewater. It was found that the efficiency of the modified sand filter was much higher than the conventional sand filter. Therefore, it can be concluded that modified sand filter can be used to remove heavy metals. It was found that agro based waste materials like groundnut shell and rice husk can be effectively used.
Experimental investigation on properties of Lightweight Concrete Blocks incorporated with Cloth pieces.
Million tons of waste clothes are deposited in landfills worldwide. To reduce the pollution caused by waste clothes, they can be incorporated into concrete. This project deals with the experimental investigation of properties of lightweight concrete blocks incorporated with cloth pieces using expanded perlite lightweight aggregate. The materials used in making concrete blocks are cement, fine aggregates, coarse aggregates, expanded perlite, old waste cloth pieces, starch and water. Old clothes originated from the household consumer sector and collected from local tailor shops are utilized for the project. They are shredded into small sizes similar to that of fine aggregate. Starch from food waste is added as a plasticizer, and which also acts as a binder. 400mm x 200mm x 200 mm moulds are used for the casting concrete blocks with cement aggregate ratio of 1:3 and w/c ratio of 0.45. Cloth pieces are added at a rate of 0.25%, 0.50%, 0.75%, and 1.0% by volume of fine aggregate. Coarse aggregates are replaced by expanded perlite by 40% of its volume. The blocks are casted and tested for block density, compressive strength, and water absorption. The results show that all of the specimens fall into the lightweight category. It was observed that at 0.25% addition of cloth pieces, the maximum compressive strength obtained was 1.96 N/mm² and 9.01 N/mm² at 7th day and 28th day respectively. Water absorption increases with increasing cloth content. The cost of a LWCB is high compared to conventional blocks. Since the load is less than conventional blocks, it can be used as partition wall, garden bench etc. Approximate 0.54 kg of cloth waste can be utilized in 1m³ of concrete.
Achievements
Project funded by The Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment (KSCSTE)
2020-2021
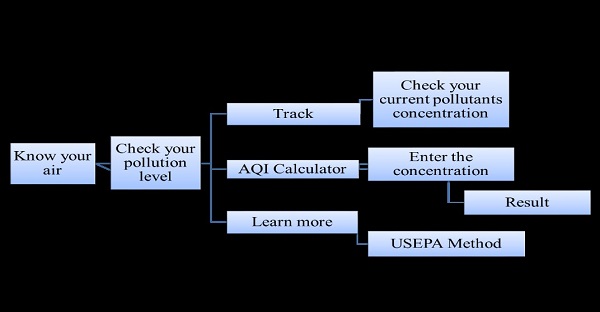
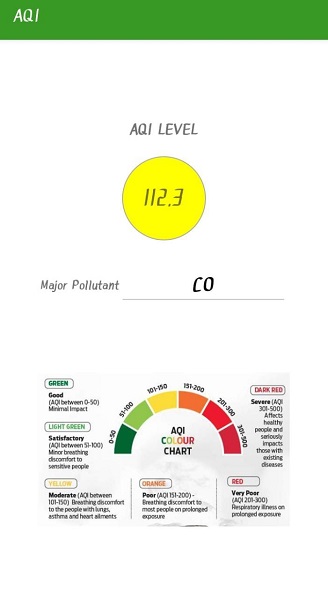
Air Quality Index (AQI) Calculator
Air Quality Index (AQI) is a simple and commonly used method to evaluate the overall air pollution of a region. The overall AQI can give clear view about ambient air and the critical pollutant mainly responsible for the quality of air, which can be easier for a common man to understand. Air Quality in various parts of Ernakulam city is being regularly monitored by Kerala State Pollution Control Board. The pollutant’s concentration data were collected and AQIs were calculated to assess the ambient air quality at three selected areas namely Eloor (Industrial), Vyttila (Commercial) and M.G. Road (Residential) areas of Ernakulam city during the year 2018, 2019 & 2020. The AQIs were calculated according to Indian Air quality Index (IND-AQI). The AQI study reveals that particulate matter (PM2.5 & PM10) was mainly responsible for maximum times in all selected areas of Ernakulam city. The AQIs obtained were used to analyse the quality of air before, during and after the lockdown 2020.A web-based AQI app using android software was developed and AQI of the selected areas were analysed. The efficiency of the AQI calculator app was validated by comparing the manually calculated AQI and AQI calculated using the application. The application was developed for quick, simple and an elegant looking response to an AQI online query.
2019-2020
FOOTAP
The students of the 2016 Batch of Civil Engineering Department, under the guidance of Prof. Lathi Karthi, Asst. Prof. Anju Paul, Asst. Prof. Sahimol Eldhose and Asst. Prof. Vidya Jose installed a FOOTAP (Foot Operated Tap) in the Canteen where there is an extensive chance of pandemics to flare-up. Though it was taken as a precautionary measure to break the spread of the infectious coronavirus, the Footap had also contributed to the reduction in wastage of water. FOOTAP consists of a table-mounted spout, pedal, and valve. The operation of this foot valve occurs by pressing leg-controlled pedals instead of hands and the water comes from the spout installed on the basin. This is a no-touch cost-effective solution. It can be installed in any public offices and the cost is around Rs1500/-. The system is characterized by its simplicity, ease of installation, and maintenance besides its low effective cost.

This is a mobile application that has been developed to evaluate the cost overrun in Kerala based construction project. The app can be used to evaluate the unexpected incurred cost or the costs that are in excess of the budgeted amount. It is a software package designed specifically for Android development. Android Studio’s job is to provide the interface to create apps and to handle much of the complicated file-management behind the scenes. The programming language used was Java and this will be installed separately on the machine. Android Studio is simply where we can write, edit and save the projects and the files that comprise different projects. The Java code allows running smoothly on Android devices and takes advantage of the native hardware. Java is needed to write the programs, the Android SDK is needed to make those programs run on Android and Android Studio has the job of putting it all together. At the same time, Android Studio also enables to run codes, either through an emulator or through a piece of hardware connected to your machine. With the help of this app we can predict the cost overrun in Kerala based construction project and thereby we can reduce the financial difficulty during construction.
Sustainable Floor Tile
Floor tiles made of clay, laterite and silica fume has been developed which shows an increase in UCC strength and water absorption. This tile can be used as a replacement to conventional floor tiles.